Fertilizer is a key resource in Rust for players looking to optimize their crop yield and build sustainable food sources. Whether you’re growing corn, pumpkins, or hemp, using fertilizer can significantly boost your farm’s efficiency.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about getting and crafting fertilizer in Rust, including materials required, how to use it effectively, and tips for maintaining a productive farm.
What Is Fertilizer in Rust?
Fertilizer is a resource used to improve the growth rate and yield of plants in Rust. It’s especially important in larger-scale farming or when food scarcity is a concern.
Applying fertilizer to planters or crop plots increases the nutrient levels in the soil, which directly benefits plant growth.
How to Get Fertilizer in Rust
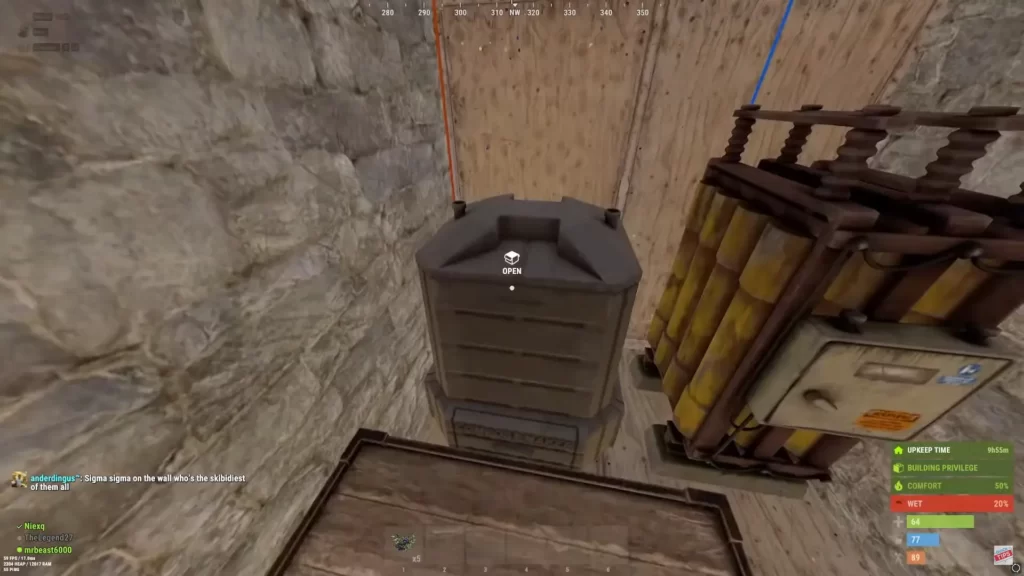
There are two primary ways to obtain fertilizer in Rust:
Crafting Fertilizer
To craft fertilizer, you’ll need to use a composter, a deployable structure that turns organic waste into usable fertilizer.
You can craft a composter using:
- 200 Wood
- 3 Metal Fragments
Once placed, the composter requires input materials such as:
- Human or animal poop
- Rotten food
- Plant matter (e.g., corn, hemp fibers)
After some time, the composter will convert these materials into fertilizer, which can be collected and used on crops.
Looting
Fertilizer can also occasionally be found in:
- Barrels
- Crates
- Sunken chests
However, looting is an unreliable source compared to crafting, and it’s not ideal for maintaining a consistent farming operation.
How to Use Fertilizer in Rust
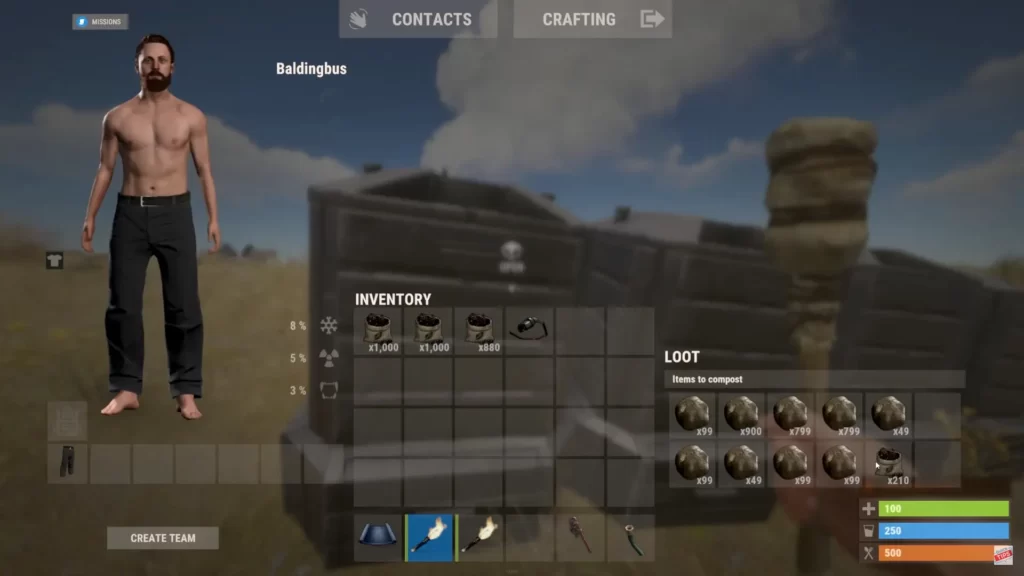
Once you’ve acquired fertilizer, you can use it in any of the following ways:
Planters and Crop Plots
- Fertilizer is added to the soil container of a planter box or crop plot.
- Open the planter’s interface and drag the fertilizer into the “Nutrients” section.
- Fertilizer affects the three key nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. Higher nutrient levels result in better growth.
Composting Cycles
Continue adding organic materials to the composter to keep a steady supply of fertilizer. Make it a routine part of your base maintenance.
Best Practices for Farming with Fertilizer

To get the most out of your fertilizer in Rust, follow these tips:
Build Multiple Composters
Having several composters running in parallel ensures a consistent supply.
Designate one for poop, one for food, and another for plant matter to optimize conversion.
Use Large Planter Boxes
Large Planters allow for multiple seeds and have more room for fertilizer storage.
They are the most efficient containers for crop yield.
Monitor Water and Light
Fertilizer alone won’t guarantee optimal growth. Make sure your plants also receive sufficient water (via sprinklers or manual watering) and light (natural or artificial).
Balance Nutrients
Not all fertilizer is the same. Monitor your soil’s nutrient levels and adjust by adding more or mixing different types of organic inputs into the composter.
Protect Your Farm
Farms attract raiders. Keep them enclosed and protected with walls, traps, and locks.
Use Genetics:
Some seeds in Rust come with genetic traits. Use crossbreeding to develop high-yield, fast-growing, or hardy plants.
Automate Your System
With solar panels, sprinklers, and smart switches, you can fully automate watering and lighting.
Schedule Crop Rotation
Just like in real farming, rotating crops and refreshing the soil helps maintain long-term fertility.
Summary
Fertilizer is a powerful asset in Rust for any player serious about farming. By crafting composters, managing your organic waste, and strategically using fertilizer, you can create a stable and productive source of food and materials.
Whether you’re growing crops for survival or profit, mastering the fertilizer system is a key step in becoming a self-sufficient Rust player. So grab that composter, gather your waste, and start building the ultimate farm today!
Frequently Asked Questions
To make fertilizer in Rust, place plant matter like food, seeds, or cloth into a composter. Over time, it converts these into fertilizer, which you can then use to enrich soil plots for farming. Ensure the composter is placed properly and regularly filled for continuous production.
You can turn dung into fertilizer by placing it into a composter. Dung is produced by animals or collected from planters with animals nearby. Add the dung to the composter along with other compostable materials. After some time, it converts into usable fertilizer for crops.
Horse dung gives the most fertilizer when placed in a composter, followed by rotten food, cloth, and seeds. Horse dung is highly efficient and yields the best composting results, making it ideal for large-scale farming setups. Prioritize collecting dung to maximize fertilizer output quickly and consistently.
You can’t directly exchange scrap for fertilizer, but you can use scrap to support farming, which leads to fertilizer production. Here’s how:
Buy seeds with scrap from Bandit Camp.
Grow crops using planters and water.
Compost leftover crops or cloth to make fertilizer.
To get fertilizer in Rust, place organic items like horse dung, spoiled food, seeds, or cloth into a composter. Over time, these materials convert into fertilizer. Horse dung produces the most. Use fertilizer to enrich planters and grow crops more efficiently. Composters can be crafted or found in the world.